
Several of the words we use often are derived from a root word. Knowing the definitions of common roots will assist you in deciphering the meanings of new words when you come across them. Traditional root words are derived from Latin and Greek and do not generally stand on their own as a complete term. As a result, ‘desire’ becomes ‘desir-,’ while ‘beauty’ becomes ‘beauty-‘ in the construction of ‘beautiful’ and the highly complicated ‘beautician.’ What Exactly Is a Root Word?Ī root word is a word or word component that serves as the foundation for new words by adding prefixes and suffixes. It’s also worth noting how, in complicated words like this, the spelling of the root can be changed to conform to the bound morphemes around it. ‘Desirable,’ on the other hand, is more complicated, mixing a root morpheme with the bound morpheme ‘-able.’ ‘Undesirability’ is much more complicated, with one root and three bound morphemes: un+desire+ability. As an example, the word ‘desire’ can be characterized as a root morpheme that forms a single word. Morphologically simple words have only one root morpheme, whereas morphologically complex words have at least one independent morpheme and any number of bound morphemes. For example, the affix -er is a bound morpheme that joins with a verb like teach to form the noun ‘one who teaches.’ Words That Are Simple And Complex Affixes, unlike roots, do not have a lexical categorization and are always linked morphemes. Roots are often associated with a lexical item, such as noun, verb, adjective, or preposition. The root is the base of the word and contains the majority of its meaning. Lexical Categories And RootsĪ complex word is made up of a root word or phrase with one or more affixes. For example, the origin of concurrent is curr, which means ‘to run,’ and is not a separate word in English or Latin. Roots are bound morphs in Latin and Greek, which means they can only emerge when related to other components. This makes it especially simple to discover the origins of words like black-bird, re-fresh, and bookish-ness.
ROOT WORD VS WORD ROOT FREE
Since a root tells us more about a word’s meaning than anything else, the first question we generally ask about a complex term is: What is its root? As in blackbird, a complex word frequently contains more than one origin.” Roots are considered free morphs because they can occur as independent words in our native and nativized language. The words cosmopolitan, microcosm are derived from the Greek root word kosmos, which means universe cosmos is also a separate root word in English.

The word is treated in English as a root word that can be used alone or in conjunction with affixes, as in centenary, bicentennial, and centipede.

Cent, for example, is derived from the Latin root word centage, which means hundred. Certain root words have evolved into free morphemes and may now be used as distinct words, while others cannot. The most common form of English root words is Latin the other two major sources are Greek and Old English.Ĭertain root words are complete words, while others are word fragments. Root is derived from Old English, which means examples and observations. It is a meaningful combination of letters.

Simply said, a word root is a word portion that means something. Word root is a semantic unit in Greek and Latin Roots.
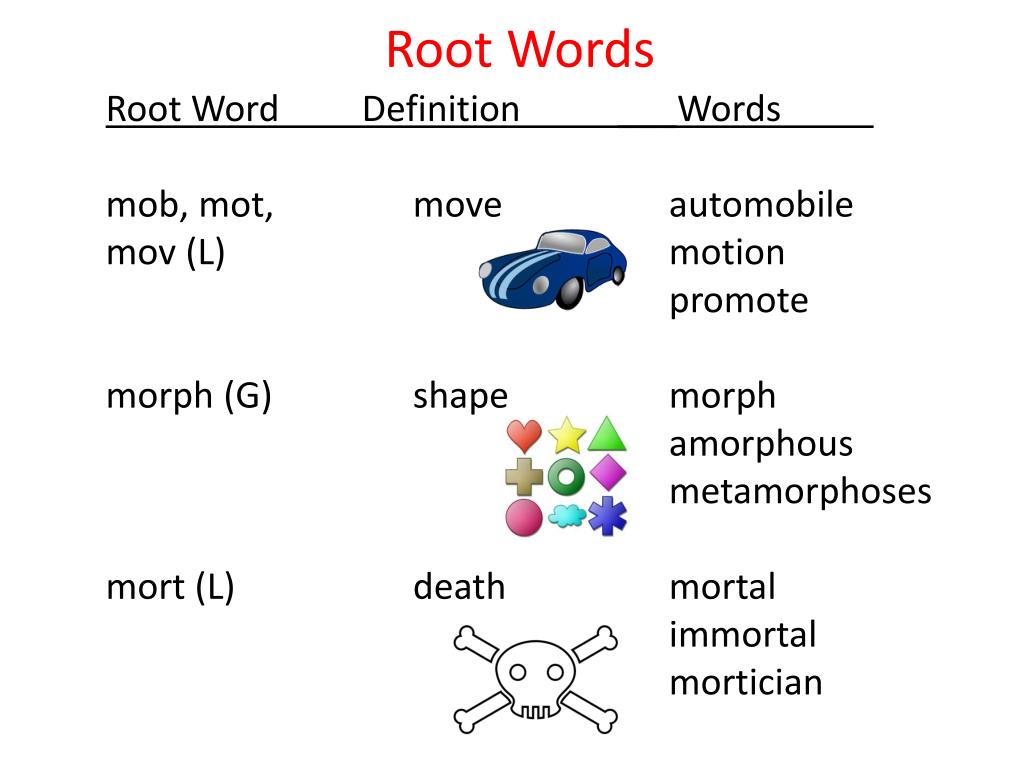
In English grammar and terminology, a root is a word or word constituent from which other phrases grow, typically by the addition of prefixes and suffixes.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
